Free radicals are also known as reactive oxygen species and are produced by the metabolism of oxygen in the body. These free radicals generated after metabolism are unstable oxygen, which is more active than oxygen due to the lack of electrons. Free radicals are continuously circulating in the body, ready to attack and grab electrons from other normal cells to stabilize themselves.
.png)
Under normal circumstances, free radicals in the human body are also used to defend against diseases. When bacteria, moulds, and viruses invade the human body, the body’s immune system will be alerted. For example, phagocytes will be catalysed by related enzymes to generate superoxide free radicals to eliminate bacteria or infected cells. Therefore, free radicals must be kept within a certain range in the body, to avoid excessive damage.
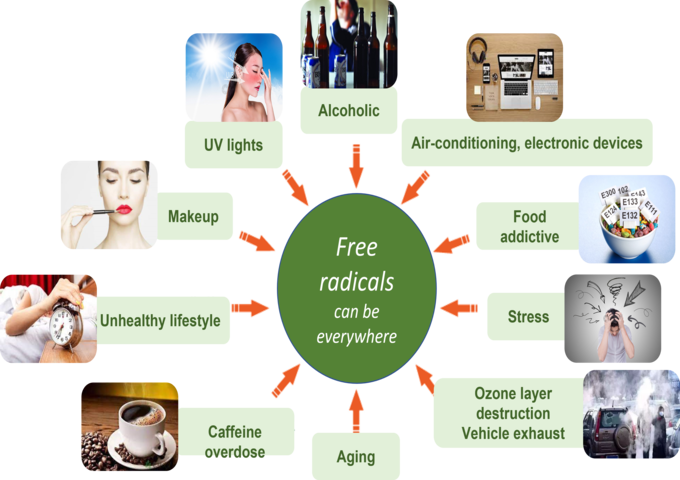
However, emerging technology at a rapid pace also affects the surrounding environment, causing more external factors to increase free radicals in the body, such as:
Once the free radicals in the body are excessive in large amounts and exceed the range of the body's normal defences, the "radicals chain reaction" occurs. For example, basic substances such as proteins, fats, and DNA are oxidized to become new free radicals, which then oxidize other cells. Such a vicious circle results in the gradual damage and deterioration of various organ functions in the human body. It accelerates aging and causes various diseases, such as:
- Nervous system diseases such as memory deterioration, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis
- Cardiovascular diseases such as ischemia, hypertension, congestive heart failure, atherosclerosis, cardiomyopathy
- Diabetes
- Lung failure
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Kidney failure
- Eye diseases
- Toxaemia of pregnancy, intrauterine growth retardation, etc.
Although there are antioxidant defence mechanisms in the human body, the ability of the body to scavenge free radicals will be weakened with age. Therefore, we should develop good habits in our daily life, and avoid sources of free radicals to combat the harm caused by free radicals. Such as always staying positive mentally and physically and avoiding excessive stress and negative emotions. Eat more foods that are rich in antioxidants including vitamins A, C, E, lycopene, and curcumin to help to remove excess free radicals in the body.