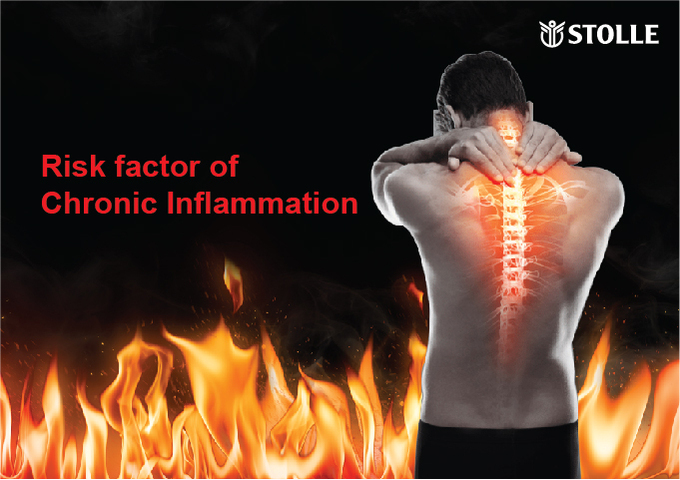
Risk factors of Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is the body's natural response to combat infections and injuries. However, when inflammation goes uncontrolled or becomes chronic, it can lead to various health issues.
Different Types of Inflammation
- Acute Inflammation: Acute inflammation is a short-term, self-limiting response that typically occurs rapidly after an infection or tissue injury. Symptoms include redness, pain, and local heat. This type of inflammation aids in clearing infections and promotes wound healing.
- Chronic Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a persistent and gradually worsening state of inflammation that can last for months or even years. Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation does not typically resolve on its own and can occur throughout the body or in specific tissues. Multiple studies have confirmed its association with various diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Mechanisms of Chronic Inflammation
The development of chronic inflammation involves multiple biological and molecular mechanisms:
- Initial Inflammatory Event: Chronic inflammation may stem from an initial inflammatory event, such as an infection, tissue injury, autoimmune response, or other inflammatory triggers. During this stage, the immune system releases inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines, to attract immune cells to address the issue.
- Overactive Immune System: In normal circumstances, the immune system recognizes and attacks infections, but an overactive state may lead to attacks on healthy tissues. This can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or prolonged exposure to irritants.
- Cellular Damage and Repair: Prolonged inflammation can cause damage to tissue cells, while immune cells attempt to repair this damage. However, in chronic inflammation, this damage and repair cycle can alternate, leading to further tissue damage and potential organ dysfunction.
- Release of Inflammatory Mediators: Chronic inflammation is often accompanied by the release of numerous inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines, chemokines, and inflammation-regulating proteins. Persistent signalling keeps the immune system continuously active. These molecules attract white blood cells to damaged tissues, intensifying inflammation. This might involve persistent infections, tissue damage, or other ongoing stimuli, such as tumor cells.
Factors Influencing Chronic Inflammation
Various factors influence the occurrence of chronic inflammation, including:
- Genetic Factors: An individual's genetic background may increase their susceptibility to chronic inflammation. Certain genetic variations have been associated with susceptibility to chronic inflammation.
- Lifestyle: Diet, exercise, body weight, smoking, and alcohol consumption significantly impact chronic inflammation. Unhealthy lifestyles may increase the risk of chronic inflammation.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and excessive stress can also trigger chronic inflammation.
Prevent Inflammation Naturally With Stolle ImmNuPlus and Stolle ImmNuPro
To reduce the risks of chronic inflammation, consider incorporating a daily dosage of Stolle ImmNuPro with 5 unique anti-inflammatory benefits, including:
- Reduce Autoimmune disease
- Reduce allergic inflammation
- Reduce joint discomfort
- Reduce intestinal inflammation
- Reduce overall inflammation
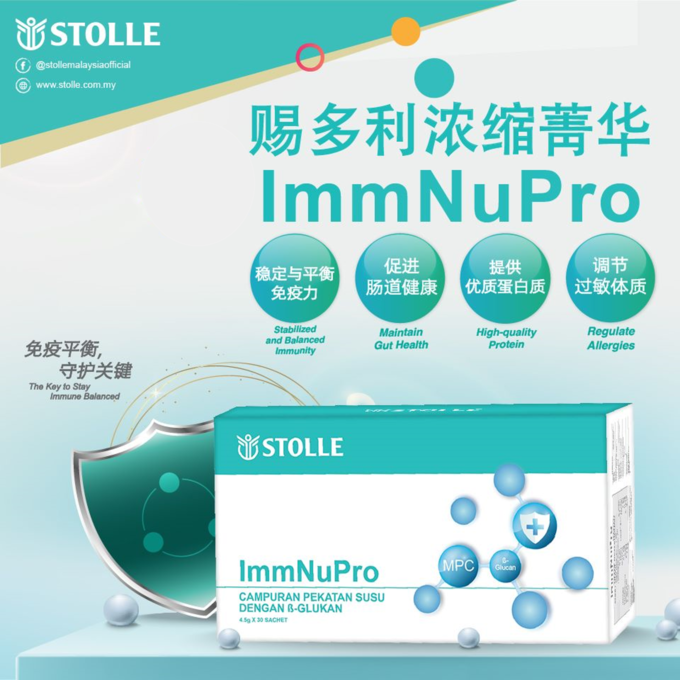
ImmNuPlus with patented bioactive factors such as specific IgG , secretory IgA, lactoferrin, and anti-inflammatory factors directly supports the immune system by balancing immune responses

Remember to enjoy a daily dose of Stolle ImmNuPro and ImmNuPlus and adopt a healthy lifestyle along with personal risk management to reduce the risk of chronic inflammation.
Immune Today, Healthy Everyday!